Database Keys
Keys
A key is a single or combination of multiple fields. Its purpose is to access or retrieve data rows from the table account to...
2 – Phase Commit Protocol
Commit Protocol
In transaction processing, databases & comp. n/w, the 2 Phase commit is a type of atomic commitment protocol ( ACP ). It...
Oracle Inside
Oracle Architecture
Basically, these are two main components of ORACLE Database Architecture.
Oracle Architecture is an Object – Relational Database Management System, provides an open comprehensive...
What is Database Transaction ?
Transaction Management
In database, transaction gins technically when 1st executable SQL statements is encountered. An executable SQL statement is encountered. An executable SQL statement generates...
Database Transaction
Database Transaction
Transaction is a Collection of operations that forms a single logical unit of work.
A transaction is an atomic unit of work that...
DBMS Client/Server Computing
Client/Server Architecture for DBMS
Client/Server Computing represents a model wherein requests are made at one end & the client end and provided at another...
DBMS vs FPS
DBMS vs FPS ( File Processing System)
Flexibility
Because programs and data are independent, programs don’t have to be modified when types of unrelated data...
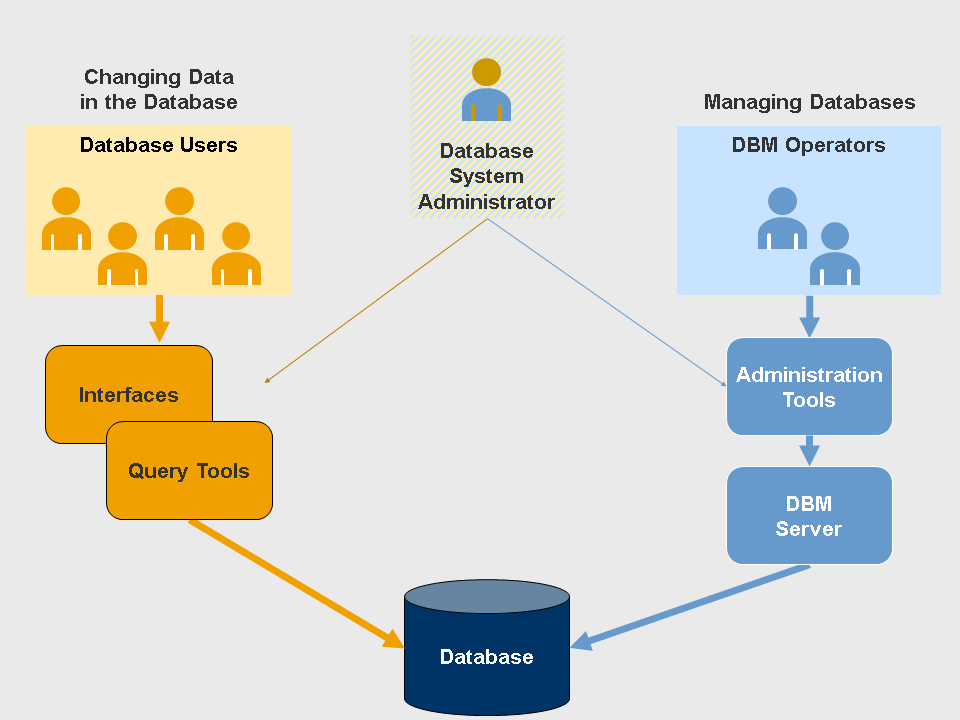
Database Users
Database End Users
End users are the people whose jobs require access to the database for querying, updating and generating reports; database primarily exists for...
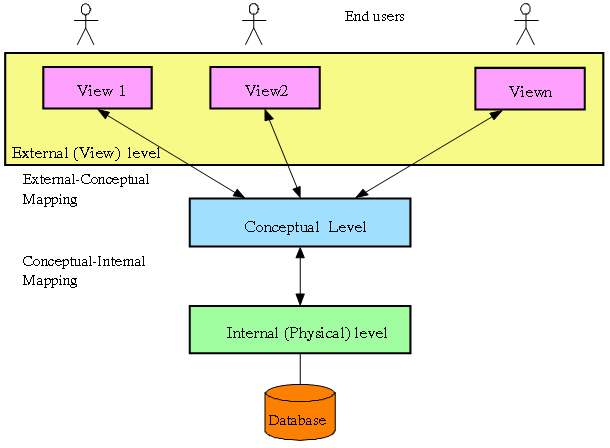
Database 3-Level Architecture
External Level :
The User’s view of the database
Consists of a no. of different external views of the DB
Describes part of the...
Database Data Structure
Data Independence
The ability of modifying a schema definition in one level without affecting a schema definition in a Higher Level is called Data...