Keys
A key is a single or combination of multiple fields. Its purpose is to access or retrieve data rows from the table account to the requirement.
- The keys are defined in the table to access / sequence the stored data quickly & smoothly.
- They are used to provides link b/w tables.
Purpose of Keys
- To ensure that each record in a table is precisely identified
- To help in establishing & enforcing various types of integrity constraints
- To establish table relationship
Types of Keys
- Super Key
- Candidate Key
- Primary Key
- Secondary/Alternate Key
- Composite/Concatenate/Compound Key
- Foreign Key
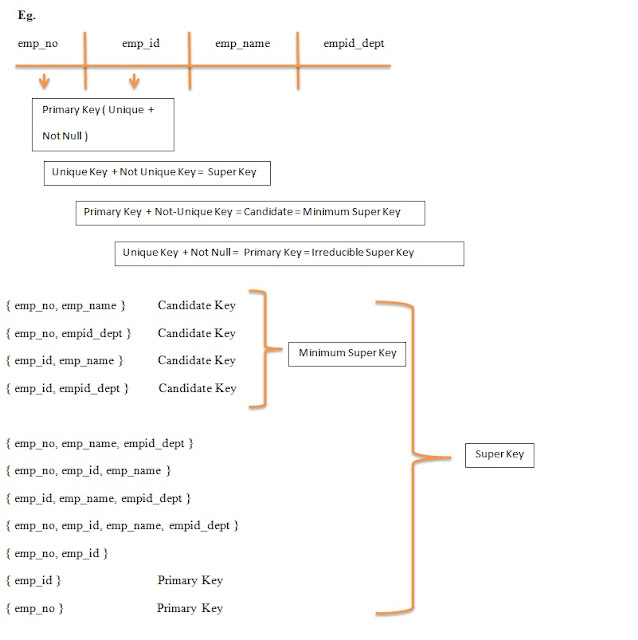
Super Key
It is a set of attributes of a relation variable for which it holds that in all relations assigned to that variable there are no two distinct tuples that have the same value for attributes in this set. A relation can have multiple superkeys.
- Super key is a key represents a column or set of columns that uniquely identifies a record.
- Any unique key with some non-unique key combination is called a superkey of that relationship.
Primary Key
- The attribute or combination of attribute that uniquely identifies a row or a record.
- It is the min. possible superkey ( irreducible super key )
- Non-redundant ( it does not have duplicate values )
Candidate Key
- The relation does not have two distinct tuples with the same values for these attributes.
- Candidate key is the min. super key which is comprised of more than one column.
There is no proper subset of these attributes for which one holds. Thus, a candidate key is a subset of Super key.
Composite/ Combination / Compound Key
Main role of Composite key is seen in case of joining two or more tables together.
- Composite primary keys are generated when no Primary key is designated in the database at time of import.
- Compound Primary keys occur when the DB schema specifically uses more than one column to form the primary key.
Eg.
Student( stu_no, stu_roll, stu_name, stu_dept ) // stu_roll is not Primary key only Unique Key
Exam( e_stu_id, e_stu_name, e_stu_per)
JOIN( stu_no, stu_roll, stu_name, stu_dept, e_stu_id, e_stu_per )
{ stu_roll,e_stu_id } Composite Key
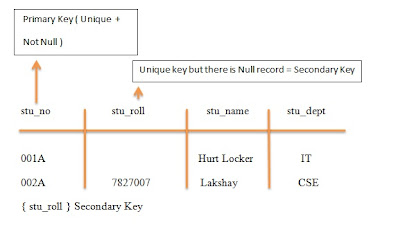
Alternate / Secondary Key ( Null + Unique )
Candidate key which is not primary key is called secondary key.
- No, such key exists technically but if in a table already has a primary key & if we need another key to be unique so, declare it as a unique but can take null values.
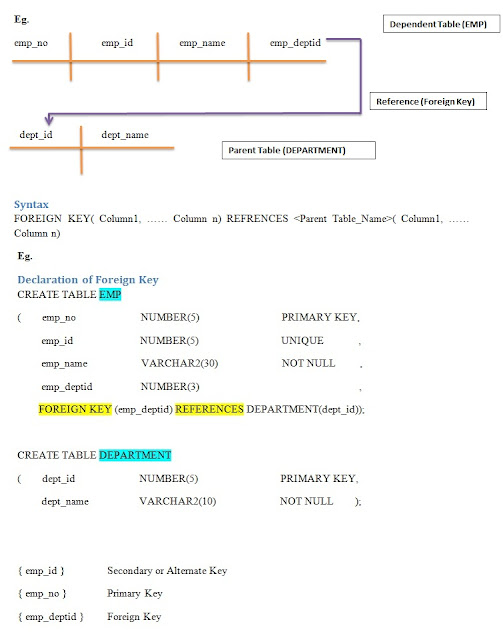
Foreign Key
- It is an attribute or combination of attribute in a relation whose values match a primary key in another table (relation)
- The Table in which a foreign key is created is called Dependent table & the table to which it refers called Parent Table.
- It is a column or set of columns that refers to a Primary key in same table or another ( connection with table or within table )
- The method provides great flexibility in linking as it is independent of the physical links b/w records.
- A table may have multiple foreign keys. For each foreign key we can have diff. table ( referenced table )