As the threats against the Internet of Things are on the rise, several types of research are going on to secure these devices.
As part of this, the Zero Day Initiative (ZDI) conducted a “Pwn2Own” competition in March. Multiple vulnerabilities were found in this competition on products belonging to many technology brands.
NetGear routers were one among the products in which vulnerabilities were reported.
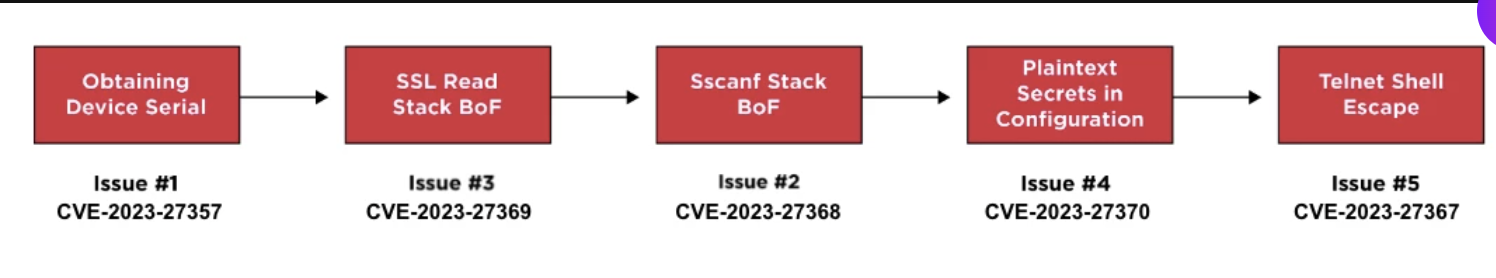
The Cybersecurity solutions firm Claroty had their team82 in this competition. The team researched NetGear RAX30 routers and found five high-severity vulnerabilities that threat actors can exploit, enabling them to conduct pre-authenticated remote code execution, command injection, or authentication bypass.
The research team found a service soap_serverd running on port 5000 (HTTP) and 5043 (HTTPS) as API servers of the router.
These handle SOAP messages about management functionality vulnerable to a stack-based buffer overflow vulnerability. All the vulnerabilities found by the research team are listed below.
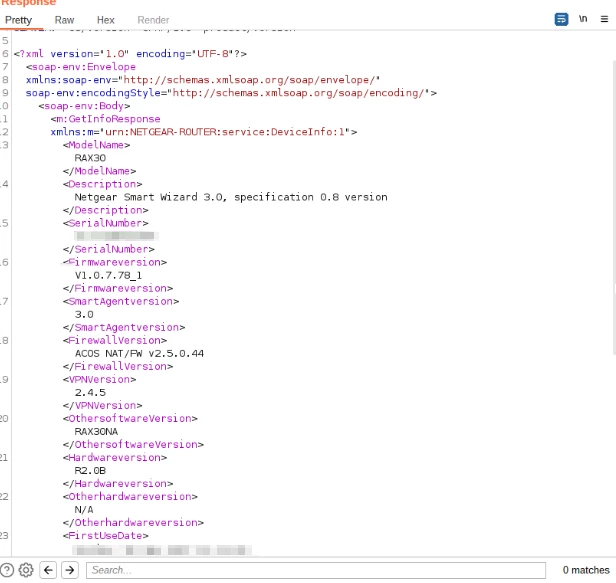
CVE-2023-27357 – Information Disclosure Vulnerability:
This vulnerability exists as there was no authentication for the “GetInfo” command. The response for this command consists of the device information such as model, serial number, firewall version, VPN version, and much more.
CVE-2023-27368: – Buffer Overflow Authentication Bypass Vulnerability
This vulnerability arises as the soap_serverd service does not check the length of the data. In addition to this, the service reads the HTTP headers first and parses them using the sscanf function to extract the method, path, and HTTP version.

Though this lack of length check allows a stack-based buffer overflow vulnerability, the HTTP receives a function that runs on port 5000 and checks the length of the HTTP header, which limits us from exploiting it. However, there was a bypass which was discovered by the research team.
CVE-2023-27369 – Buffer Overflow Authentication Bypass Vulnerability
As mentioned earlier, two ports, 5043 (HTTPS or SSL) and 5000 (HTTP), run the soap_serverd service. Therefore, both ports had two different socket read and socket write functions.
In connection with the previous vulnerability (CVE-2023-27368), the SOAP message read by the 5043 port calls a socket read function which does not check how many bytes were read.
This socket read function can conduct a stack overflow by sending a large amount of data to be read, resulting in a stack-based buffer overflow.
CVE-2023-27370 – Bypass to Reset the Admin Password
While setting up the router, the users are requested to create a unique password for authenticating into the router dashboard. Along with this, some security questions must also be set for resetting the password in case the users forget their passwords.
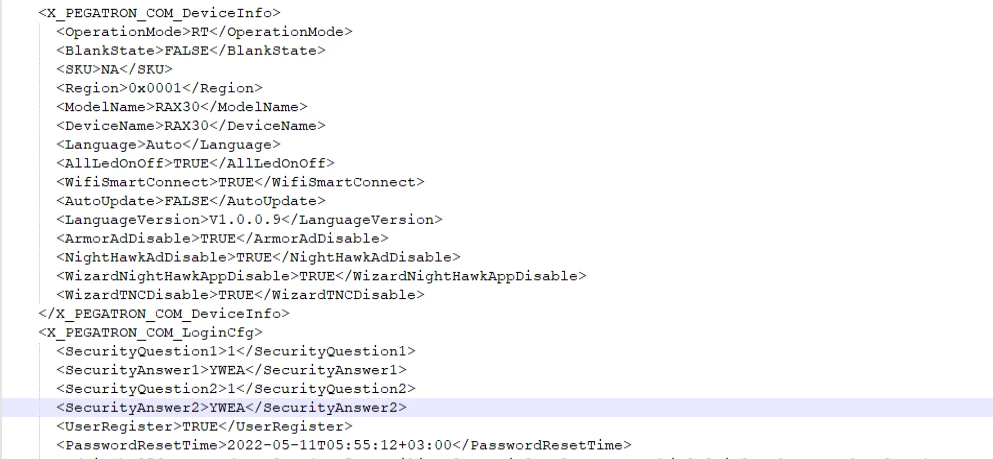
The device configuration stores this information as plain text (base64).
To reset the password, the users need to enter the router’s serial number and answer the security questions previously set.
Using the three vulnerabilities mentioned above, an attacker can bypass the authentication and run the GetConfigInfo command, which returns all the information required for resetting the administrator password.
CVE-2023-27367 – Authentication Bypass and Command Injection
The telnet service on port 23 is not enabled by default on NetGear routers. A vulnerability was discovered previously, which exists on the libcms_cli module that does not validate user-supplied commands before executing the system call.
The research team used an “open-telnet-magic-packet” to enable port 23 on the router. But still, the Telnet is restricted to specific commands.
They discovered that the TFTP command is not filtered before it is executed, which is connected with CVE-2023-27370. Hence, this TFTP interface can be used to run any command.
These five vulnerabilities are chained, which can exploit the RAX30 to enable remote command execution. Successful exploitation by a threat actor can lead to monitoring the user’s activity, redirecting traffic to malicious websites controlled by the attacker, hijacking an internet connection, or injecting malware into the network traffic.
NETGEAR has released security advisories for these vulnerabilities and requested their customers upgrade their RAX30 routers to fix these vulnerabilities.
Struggling to Apply The Security Patch in Your System? –
Try All-in-One Patch Manager Plus
Source: gbhackers.com












