An Israeli cybersecurity company, Astrix’s Security Research Group, discovered a 0-day vulnerability in Google’s Cloud Platform (GCP) dubbed Ghosttoken on June 19, 2022, which impacts all Google users.
The “GhostToken” vulnerability could enable threat actors to make a malicious application “invisible and unremovable,” ultimately rendering the victim’s Google account permanently infected with a trojan app.
On April 7, 2023, Google formally issued a patch for the GhostToken vulnerability. The malicious apps could be made invisible by attackers after being authorized and linked to an OAuth token that grants them access to the Google account.
Attackers can hide their malicious application from the victim’s Google account application management page by using the GhostToken vulnerability.
The exploit makes the malicious app unremovable from the Google account. So, the attacker holds a ‘ghost’ token to the victim’s account.
“Since this is the only place Google users can see their applications and revoke their access, the exploit makes the malicious app unremovable from the Google account,” Astrix Security researchers said.
“Since the application is entirely hidden from the victim’s view, they are prevented from even knowing their account is at risk in the first place, and even if they do suspect it – they can’t do anything but create a brand new Google account.”
How is a GhostToken utilized?
Researchers say attackers might be able to read the victim’s private Gmail messages, access their files on Google Drive and Google Photos, view upcoming events on their Google calendar, find them using Google Maps, and give access to the victim’s Google Cloud Platform services depending on the permissions victims grant the malicious app.
In the worst-case scenario, attackers may be able to remove files from Google Drive, send emails from the victim’s Gmail account to undertake social engineering attacks, steal sensitive data from Google Calendar, Photos, or Docs, and more.
Particularly, attackers merely needed to delete the associated GCP project to put the malicious applications authorized by the victims into a “pending deletion” state to conceal them.
However, following the project’s restoration, they would be given a refresh token to retrieve a fresh access token to access the victims’ data.
These actions could be performed endlessly, enabling the attackers to delete and restore the GCP project each time they required access to the victim’s data to conceal the malicious app.
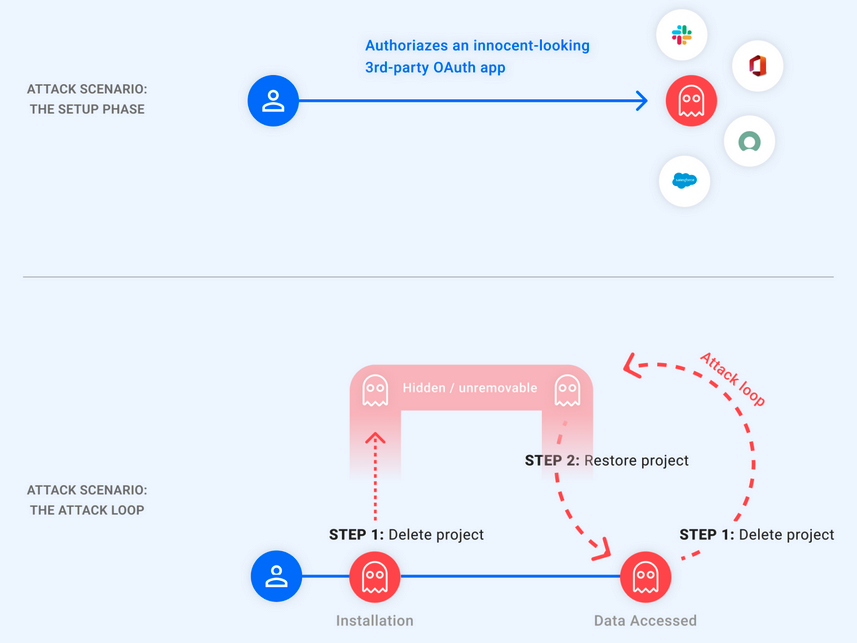
GhostToken Attack Flow
With the help of Google’s patch, GCP OAuth applications in ‘pending deletion’ states can now be removed by users from the ‘Apps with access to your account’ page, thereby preventing account takeover attempts.
Astrix advises Google users to check all authorized third-party apps on their “account’s app management page” to ensure they only have the permissions required to function.
“In today’s world of commonplace attacks,complicated threatt scenarios, and exponentially increased attack surfaces, routine security checks that clear out any unnecessary, unused, or over-privileged 3rd-party access must also look for GhostToken-like vulnerabilities”, researchers say.
Building Your Malware Defense Strategy – Download Free E-Book
Source: gbhackers.com











