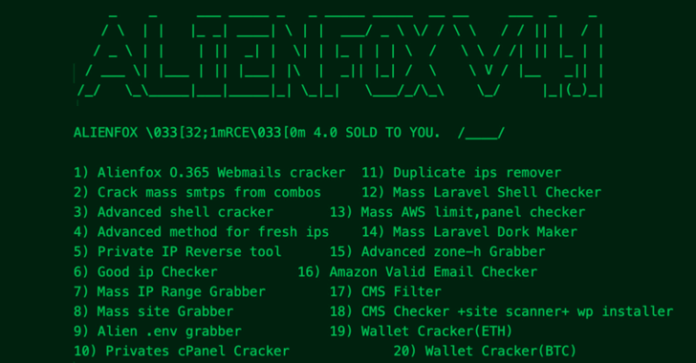
A new “comprehensive toolset” called AlienFox is being distributed on Telegram as a way for threat actors to harvest credentials from API keys and secrets from popular cloud service providers.
“The spread of AlienFox represents an unreported trend towards attacking more minimal cloud services, unsuitable for crypto mining, in order to enable and expand subsequent campaigns,” SentinelOne security researcher Alex Delamotte said in a report shared with The Hacker News.
The cybersecurity company characterized the malware as highly modular and constantly evolving to accommodate new features and performance improvements.
The primary use of AlienFox is to enumerate misconfigured hosts via scanning platforms like LeakIX and SecurityTrails, and subsequently leverage various scripts in the toolkit to extract credentials from configuration files exposed on the servers.
Specifically, it entails searching for susceptible servers associated with popular web frameworks, including Laravel, Drupal, Joomla, Magento, Opencart, Prestashop, and WordPress.
Recent versions of the tool incorporate the ability to establish persistence on an Amazon Web Services (AWS) account and escalate privileges as well as automate spam campaigns through the compromised accounts.
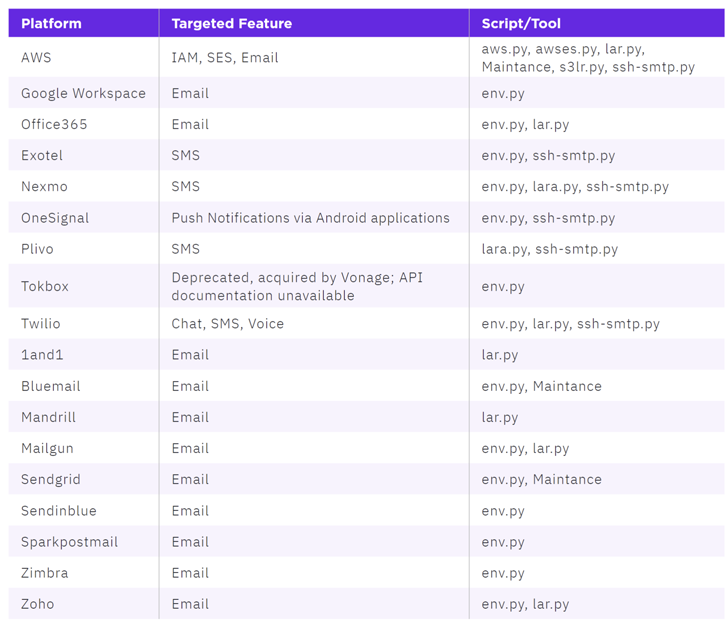
Attacks involving AlienFox are said to be opportunistic, with the scripts capable of gathering sensitive data pertaining to AWS, Bluemail, Exotel, Google Workspace, Mailgun, Mandrill, Microsoft 365, Sendgrid, Twilio, Zimbra, and Zoho.
Two such scripts are AndroxGh0st and GreenBot, which were previously documented by Lacework and Permiso p0 Labs.
While Androxgh0st is designed to parse a configuration file for specific variables and pull out their values for follow-on abuse, GreenBot (aka Maintance) contains an “AWS persistence script that creates a new administrator account and deletes the hijacked legitimate account.”
Maintance further incorporates licensing checks, suggesting that the script is being offered as a commercial tool, and the ability to perform reconnaissance on the web server.
SentinelOne said it identified three different variants of the malware (from v2 to v4) dating back to February 2022. A notable functionality of AlienFoxV4 is its ability to check if an email address is already linked to an Amazon.com retail account, and if not, create a new account using that address.
To mitigate threats posed by AlienFox, organizations are recommended to adhere to configuration management best practices and follow the principle of least privilege (PoLP).
“The AlienFox toolset demonstrates another stage in the evolution of cybercrime in the cloud,” Delamotte said. “For victims, compromise can lead to additional service costs, loss in customer trust, and remediation costs.”
Source: thehackernews.com