Lynis is an open source security auditing tool. Its main goal is to audit and harden Unix and Linux based systems. It scans the system by performing many security control checks. Examples include searching for installed software and determine possible configuration flaws.
Many tests are part of common security guidelines and standards, with on top additional security tests. After the scan, a report will be displayed with all discovered findings. To provide you with initial guidance, a link is shared with the related Lynis control.
Lynis is one of the most trusted automated auditing tool for software patch management, malware scanning and vulnerability detecting in Unix/Linux based systems. This tool is useful for auditors, network and system administrators, security specialists and penetration testers.
Intended audience:
Lynis assists auditors in performing Basel II, GLBA, HIPAA, PCI DSS and SOX (Sarbanes-Oxley) compliance audits.
Security specialists, Penetration Testers, System auditors, System/network managers, Security Engineers.
Lynis is compatible with many Operating Systems, such as:
- AIX
- Arch Linux
- BackTrack Linux
- CentOS
- Debian, DragonFlyBSD
- Fedora Core, FreeBSD
- Gentoo
- HPUX
- Kali, Knoppix
- Linux Mint
- MacOS X, Mageia, Mandriva
- NetBSD
- OpenBSD, OpenSolaris, openSUSE, Oracle Linux
- PcBSD, PCLinuxOS
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) and derivatives
- Sabayon, Scientific Linux, Slackware, Solaris 10, SuSE
- TrueOS
- Ubuntu and derivatives
Lynis can also be auditing software such as :
- Database servers: MySQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL
- Time daemons: dntpd, ntpd, timed
- Web servers: Apache, Nginx
Once lynis starts scanning your system, it will perform auditing in a number of categories:
- System tools: system binaries
- Boot and services: boot loaders, startup services
- Kernel: run level, loaded modules, kernel configuration, core dumps
- Memory and processes: zombie processes, IO waiting processes
- Users, groups and authentication: group IDs, sudoers, PAM configuration, password aging, default mask
- Shells
- File systems: mount points, /tmp files, root file system
- Storage: usb-storage, firewire ohci
- NFS
- Software: name services: DNS search domain, BIND
- Ports and packages: vulnerable/upgradable packages, security repository
- Networking: nameservers, promiscuous interfaces, connections
- Printers and spools: cups configuration
- Software: e-mail and messaging
- Software: firewalls: iptables, pf
- Software: webserver: Apache, nginx
- SSH support: SSH configuration
- SNMP support
- Databases: MySQL root password
- LDAP services
- Software: php: php options
- Squid support
- Logging and files: Syslog daemon, log directories
- Insecure services: inetd
- Banners and identification
- Scheduled tasks: crontab/cronjob, atd
- Accounting: sysstat data, auditd
- Time and synchronization: ntp daemon
- Cryptography: SSL certificate expiration
- Virtualization
- Security frameworks: AppArmor, SELinux, security status
- Software: file integrity
- Software: malware scanners
- Home directories: shell history files
How Lynis works:
In this Kali Linux Tutorial , To run it for the first time, it is recommended to use -c paramater. -c parameter means doing all tests to check the systems. If you want to put the Auditor name, just add –auditor parameter there. Here’s some
Download and Install the Lynis from GitHub
git clone
$ cd lynis-2.7.3
# ./lynis
samples output :
Once Installed then Start with Auditor or Pentester name .
# lynis -c –auditor “BALAJI”
Figure 1. Initialize
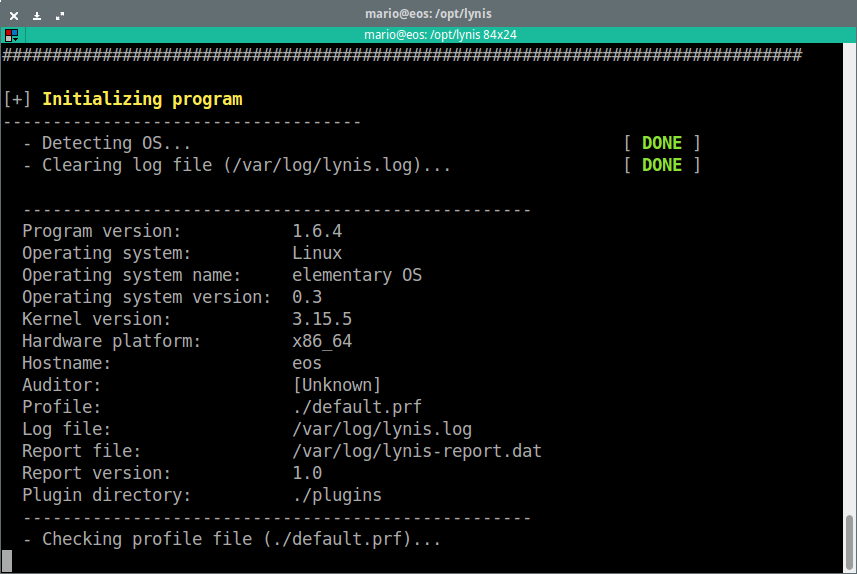
Figure 2. System Tools
Figure 3. Boot & Services and Kernel
Figure 4. Users and Group
Figure 5. Shell and storage
Figure 6. Software, Ports and Packages
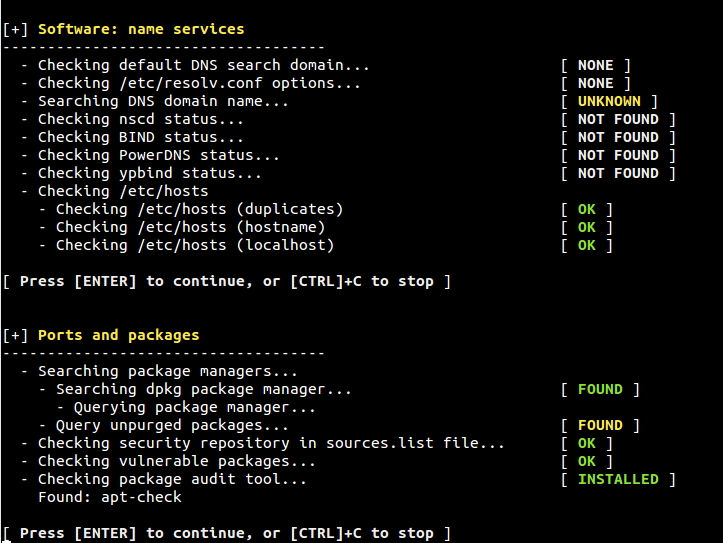
Figure 7. Networking and Printer
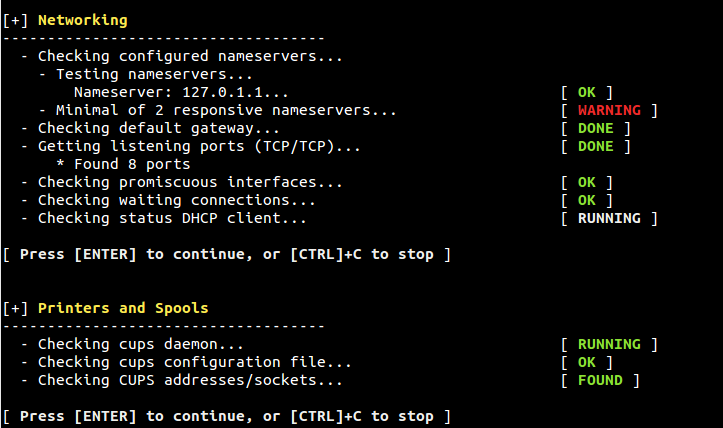
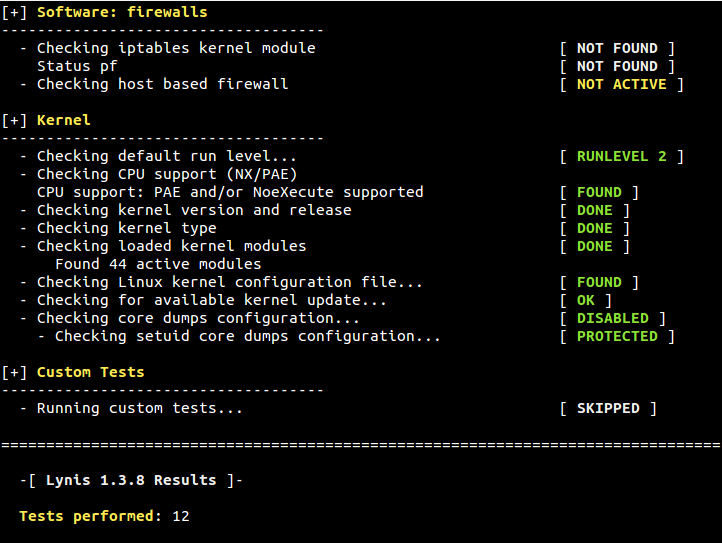
Figure 8. Email, Firewalls and Web Server
Figure 9. SSH, SNMP and Databases
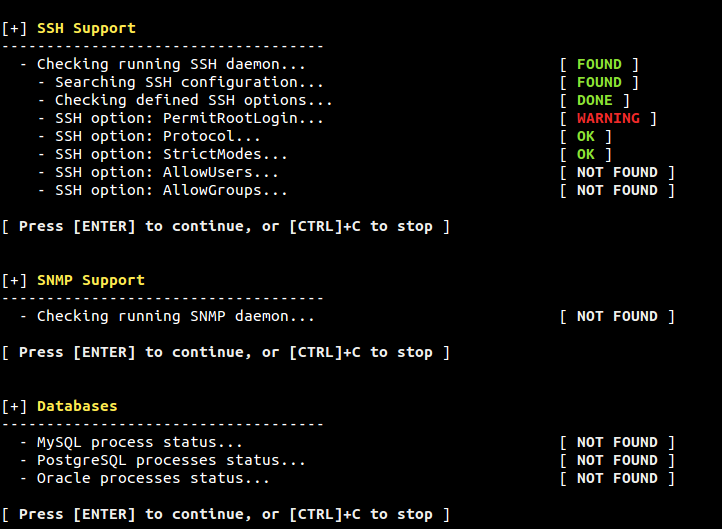
Figure 10. PHP, Squid Proxy and Logging
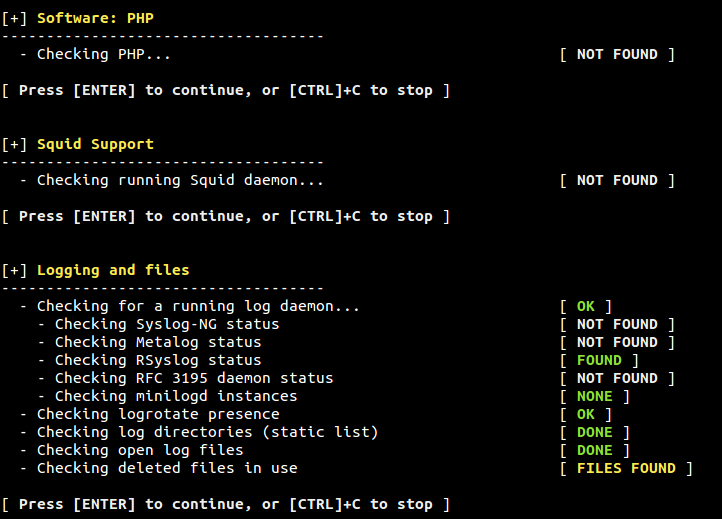
Figure 11. Inetd, Banner and Cron
Figure 12. Accounting, NTP and Cryptography
Figure 13. Virtualization, Security Frameworks and File Integrity
Figure 14. Malware Scanners, System Tool and Home directory
Figure 15. Kernel Hardening
Figure 16. Hardening, Custom Tests and Result
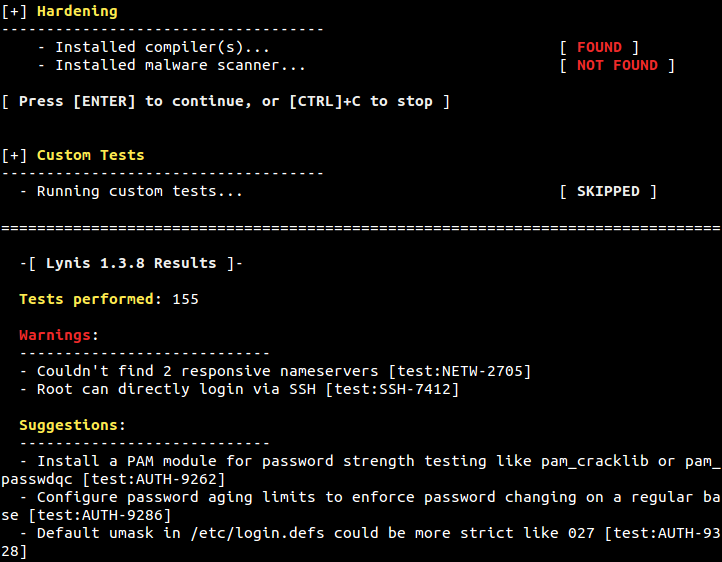
Figure 17. Hardening Index
Run Lynis with Custom Tests
Your system may not need to run all the tests. If your server not running a web server, you don’t need to test it. For this purpose, we can use –tests parameter. The syntax is :
# lynis –tests “Test-IDs”
there are more than 100 tests that we can do. Here are some list of Lynis Tests-ID.
- FILE-7502 (Check all system binaries)
- BOOT-5121 (Check for GRUB boot loader presence).
- BOOT-5139 (Check for LILO boot loader presence)
- BOOT-5142 (Check SPARC Improved boot loader (SILO))
- BOOT-5155 (Check for YABOOT boot loader configuration file)
- BOOT-5159 (Check for OpenBSD i386 boot loader presence)
- BOOT-5165 (Check for FreeBSD boot services)
- BOOT-5177 (Check for Linux boot and running services)
- BOOT-5180 (Check for Linux boot services (Debian style))
- BOOT-5184 (Check permissions for boot files/scripts)
- BOOT-5202 (Check uptime of system)
- KRNL-5677 (Check CPU options and support)
- KRNL-5695 (Determine Linux kernel version and release number)
- KRNL-5723 (Determining if Linux kernel is monolithic)
- KRNL-5726 (Checking Linux loaded kernel modules)
- KRNL-5728 (Checking Linux kernel config)
- KRNL-5745 (Checking FreeBSD loaded kernel modules)
- [04:57:04] Reason to skip: Test not in list of tests to perform
- KRNL-5770 (Checking active kernel modules)
- KRNL-5788 (Checking availability new kernel)
- KRNL-5820 (Checking core dumps configuration)
Below is a sample command to run Check uptime of system and Checking core dumps configuration tests. If you want to add more tests, just add more Test-ID separated by space.
# ./lynis –tests “BOOT-5202 KRNL-5820”
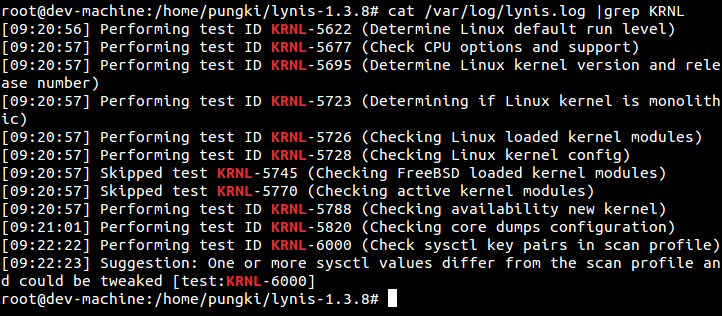
To get more Tests-IDs, you can find it inside /var/log/lynis.log. Here’s a trick how to do it.
1. First, we need to run lynis with -c (check-all) parameter.
# ./lynis -c -Q
2. Then look at inside /var/log/lynis.log file. Use cat command and combine it with grep. Let say you want to search Test-ID which related to Kernel. Use keyword KRNL to find it.
# cat /var/log/lynis.log | grep KRNL
Below is a complete keywords of Test-IDs that available in Lynis.
BOOT
KRNL (kernel)
PROC (processor)
AUTH (authentication)
SHLL (shell)
FILE
STRG (storage)
NAME (dns)
PKGS (packaging)
NETW (network)
PRNT (printer)
MAIL
FIRE (firewall)
HTTP (webserver)
SSH
SNMP
DBS (database)
PHP
LDAP
SQD (squid proxy)
LOGG (logging)
INSE (insecure services – inetd)
SCHD (scheduling – cron job)
ACCT (accounting)
TIME (time protocol – NTP)
CRYP (cryptography)
VIRT (virtualization)
MACF (AppArmor – SELINUX)
MALW (malware)
HOME
HRDN (hardening)
Run lynis with categories
If you feel that put a lot of Test-IDs is painful, you can use –test-category parameter. With this option, Lynis will run Test-IDs which are included inside a specific category. For example, you want to run Firewall and Kernel tests. Then you can do this :
# ./lynis –tests-category “firewalls kernel”
Run Lynis as Cronjob
Since security needs consistency, you can automate Lynis to run periodically. Let’s say you want to run it every month to see if there is any improvement since the last Lynis run. To do this, we can run Lynis as a cronjob. Here’s a sample cronjob to run it every month.
#!/bin/sh
AUDITOR=”automated”
DATE=$(date +%Y%m%d)
HOST=$(hostname)
LOG_DIR=”/var/log/lynis”
REPORT=”$LOG_DIR/report-${HOST}.${DATE}”
DATA=”$LOG_DIR/report-data-${HOST}.${DATE}.txt”
cd /usr/local/lynis
./lynis -c –auditor “${AUDITOR}” –cronjob > ${REPORT}
mv /var/log/lynis-report.dat ${DATA}
# End
Save the script into /etc/cron.monthly/lynis. Don’t forget to add related paths (/usr/local/lynis and /var/log/lynis), otherwise the script will not work properly.
You can follow us on Linkedin, Twitter, Facebook for daily Cybersecurity updates also you can take the Best Cybersecurity courses online to keep your self-updated.
Source: gbhackers.com