Check Point Research has recently published a study revealing the discovery of a previously unknown malware variant dubbed FluHorse.
The malware comprises multiple malicious Android apps that impersonate legitimate ones, and unfortunately, most of these fake apps have already been installed by over 1,000,000 users.
All these malicious applications are designed to steal victims’ credentials and 2FA codes, compromising their personal and sensitive information.
FluHorse targets various industries across the Eastern Asian market and is distributed through email.
These attacks can prove persistent, dangerous, and challenging to detect, as they often leverage email accounts belonging to high-profile entities during the initial stages.
Mimicked Apps
Attackers find applications that mimic trusted, reputable companies particularly enticing since they are likely to attract financially capable customers.
The legitimacy of these copied applications makes them even more appealing to hackers.
- ETC with 1,000,000+ Google Play installsVPBank
- Neo with 1,000,000+ Google Play installs
According to the ETC APK developer’s website, the application generates approximately 16 million transactions daily, with over 6 million users relying on its services.
VPBank, a major private bank in Vietnam, recorded total assets surpassing 631 trillion dongs as of December 2022, cementing its position as one of the country’s biggest financial institutions.
While the enterprise encompasses a diverse range of financial services like:-
- Spanning retail
- Corporate
- Consumer Finance
- Wealth management operations
Also, experts have noted the presence of other malicious dating applications’ presence. However, they have not discovered any corresponding applications that the malware attempts to impersonate.

Infection Chain
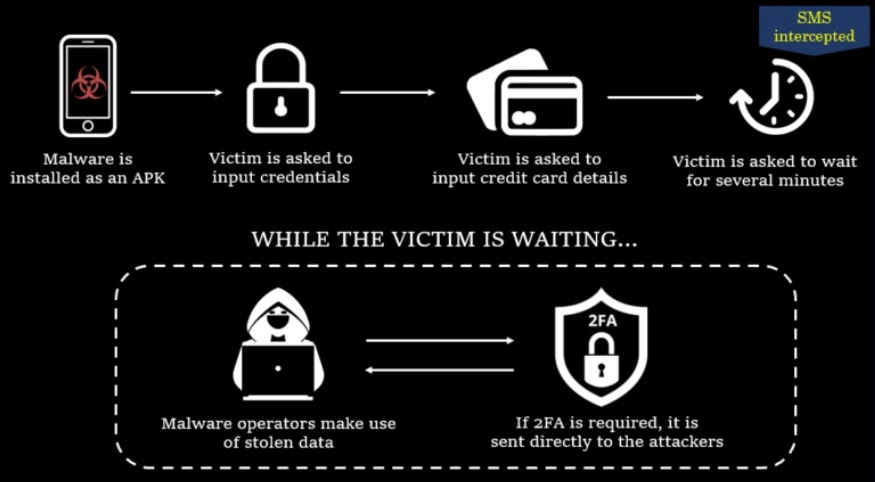
The malicious applications contain nothing beyond multiple window replicas that offer the victim input options.
While the scheme’s effectiveness remains undisputed, regardless of the attackers’ intentions, once the victim enters their sensitive data, the information is swiftly exfiltrated to the command and control (C&C) server.
Upon reaching this step, the SMS interception feature takes over, redirecting all incoming SMS traffic to the server under the attacker’s control.
The malware actors intercept any Two Factor Authentication (2FA) codes when prompted in the event they have already entered stolen credentials or credit card data.
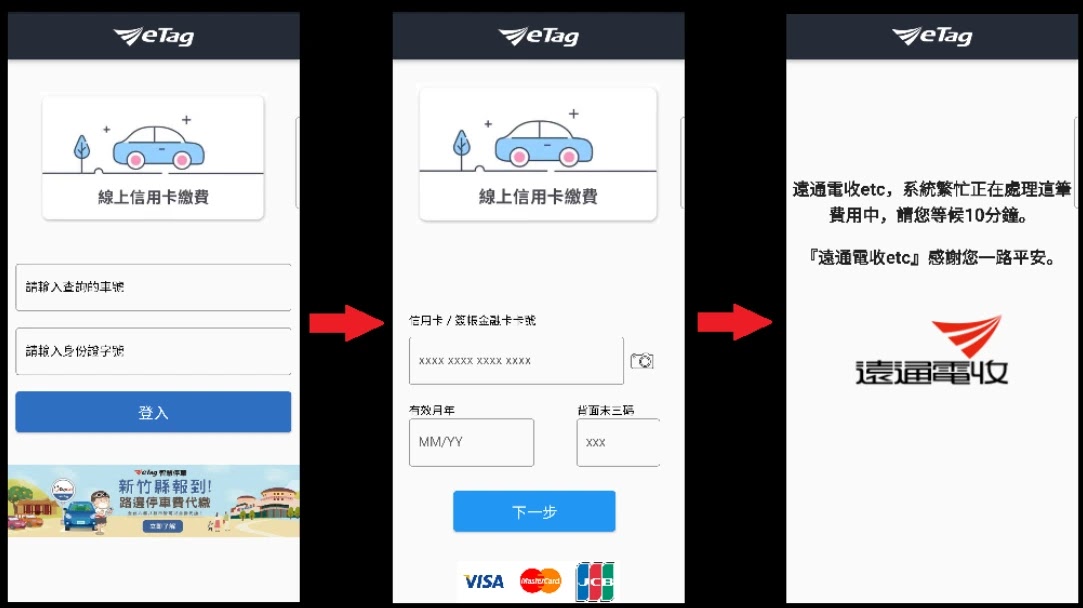
Moreover, the email lures serve as an effective social engineering tactic and are consistent with the supposed intent of the malicious APK (like paying tolls) installed afterward.
To achieve the objective, assessing Flutter-based applications requires intermediate steps compared to analyzing pure Android apps.
The Flutter framework uses a custom virtual environment that enables developers to develop across multiple platforms using a single code set.
The Flutter platform utilizes a particular programming language called Dart for its development. At the same time, the availability of the Flutter platform code as an open-source project makes analysis somewhat more straightforward.
The malicious samples have multiple layers of technical implementation. Despite the simple, functional aspect, analysts deduce that the malware developers utilized Flutter as a developing platform, indicating minimal programming effort.
Since May 2022, FluHorse activity has been under the radar of cybersecurity researchers. Their analysis reveals the persistent danger of these campaigns as fresh infrastructure nodes and malicious applications surface every month.
Struggling to Apply The Security Patch in Your System? –
Try All-in-One Patch Manager Plus
Source: gbhackers.com












